On-page SEO, also known as on-site SEO, is the way to optimize content pieces to rank higher in search results. Hence, your website gets organic traffic from Google.
There are 10 on-page practices to optimize a web page. These include content quality, images, internal and external links, and title tags.
However, on-page SEO is only one of the three main SEO types. Other factors that affect your content’s ranking include backlinks and technical aspects. Therefore, you must not depend only on one type of optimization.
On-Page SEO vs. Off-Page SEO
People often get confused with the two terms — ‘On-Page SEO’ and ‘Off-Page SEO’. Since both are said to be crucial for ranking, let me explain them quickly to you.
- On-page SEO is about anything you do within your site. This includes the images, content, and headings.
- Off-page SEO is about things that you do outside of your site to improve your ranking. This includes getting backlinks, guest posting, and social media marketing.
Both are crucial to a good SEO strategy.

Why is On-Page SEO Important?
Over the years, Google’s algorithm has prioritized high-quality content that serves people just right. Google’s latest update states that it prioritizes high-quality, unique content that meets a user’s search intent.
And…content is a part of on-page SEO.
Search engines like Google crawl the content to check if it meets a keyword’s user intent and fulfills on-page SEO elements. Therefore, good content ends up ranking on the first page.
Read more: Yoast SEO Plugin Guide
10 On-Page Optimization Techniques
Now that we know why on-site SEO is important, here are 11 key techniques you should consider:
- Publish reader-focused content
- Place target keywords strategically
- Write keyword-rich title tags
- Structure your page with headings and subheadings
- Write a hook, not a description
- Add internal links
- Add external links
- Optimize with images
- Complete the word count
- Make the URL slug SEO-friendly
1. Publish reader-focused content
As I’ve said earlier too, publish unique content (learn content writing) that’s helpful to your ideal reader. That’s why, the first step is to collect keywords and figure out the search intent before writing anything.
So, how do you find what your reader’s search intent is?
The answer is; from the keywords research.
Tools such as SEMrush can help you here. For instance, if I search for the keyword “Best books for beginners”, here’s what I get:
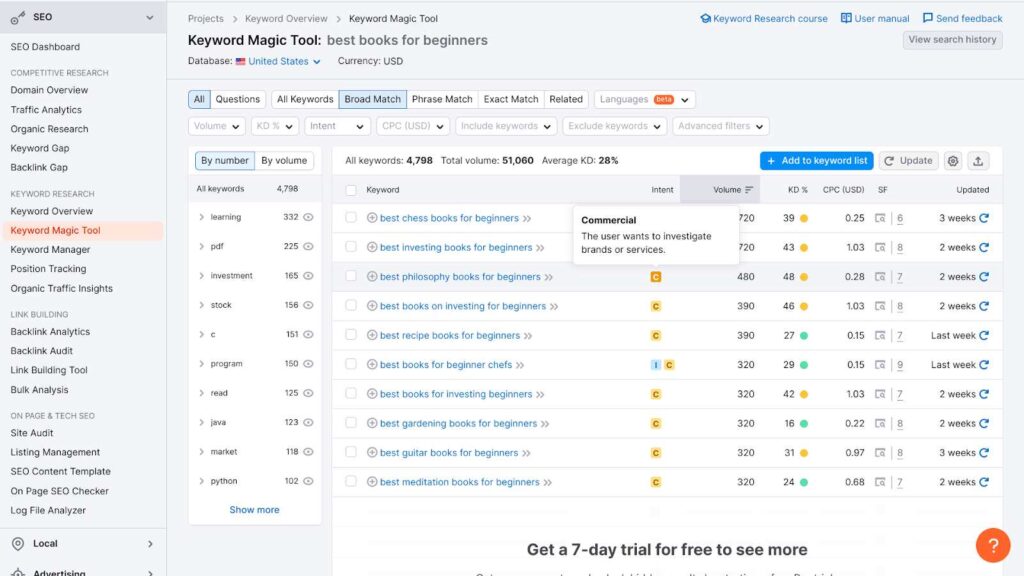
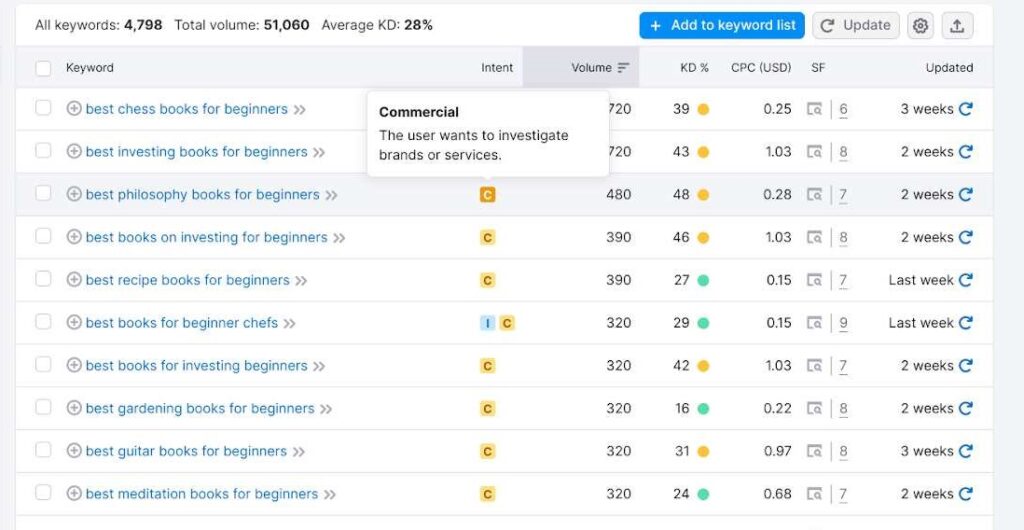
It says that the user has a commercial intent. Meaning, the user wants to know a few books’ names.
It also shows the keyword difficulty percentage, monthly search volume, and CPC. Assuming that you’re just starting with a brand new website, I suggest targeting long-tail keywords (like the one I chose).
As you can see, long-tail keywords have a low keyword difficulty rate (0-30). They’re easy to target and thus, they’re green.
Once you know the reader’s intent, start crafting the first draft.
2. Place target keywords strategically
Google has blacklisted sites that stuffed their content with keywords a long time ago. It’s a bad optimization tactic. That’s why you need to learn to place keywords strategically rather than stuffing them like cheese in bread.
The best places to spread your keywords are:
- H1
- Subheaders (H2, H3, H4)
- First paragraph
You should also include keywords throughout the content naturally. However, remember not to overoptimize the content by adding too many keywords in the subheadings and paragraphs.
3. Write keyword-rich title tags
Title tags indicate the title of a page. This title of the page is displayed in social media posts, search engines, and browser tabs.
A click-worthy title tag increases the click-through rate (CTR) from users coming organically. Here’s what it looks like:
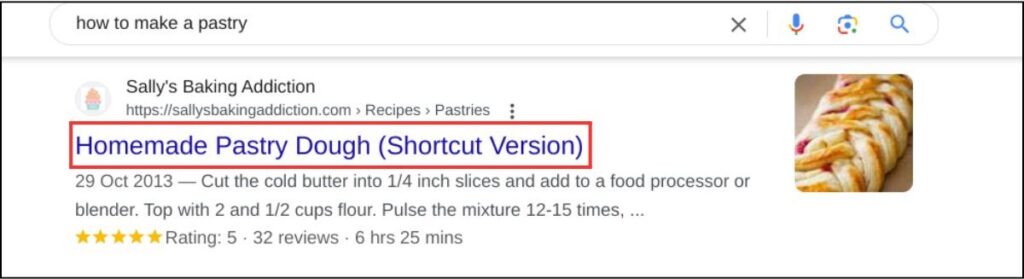
Follow these 3 tips to write a good title:
- Keep it short: Make sure that your title is 50-60 characters long.
- Include the target keyword: Try to include it at the beginning as it’ll help Google understand the context of your page.
- Make it unique: Don’t copy or duplicate someone else’s blog title. Google never liked a duplicated content piece.
4. Structure your page with headings and subheadings
Don’t make the mistake of filling your page with paragraphs but no headings or subheadings. Here’s why:
- It’s not easy for the readers to skim through it.
- Google cannot understand your page’s structure or its intent. Hence, the algorithm won’t consider ranking it.
So, here’s what you should do:
- Add your target keyword and its variations in some of your headings (H2, H3).
- Use H1 as the title (the main topic). Then, use H2 for subtopics and H3 for sub-subtopics. (learn how to add heading in Elementor)
You can understand better with this image:
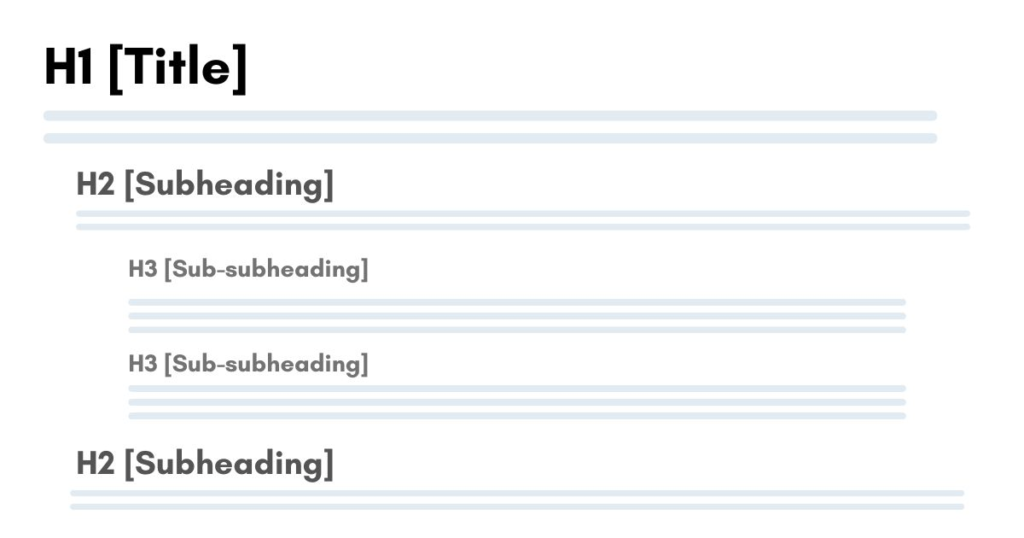
5. Write a hook, not a description
A meta description is a snippet that describes what a web page is all about. It shows up on SERP results and looks like this:
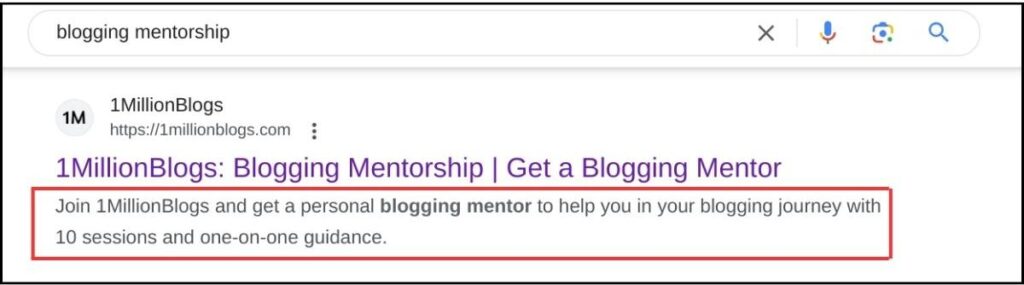
Meta descriptions may not directly influence a page’s ranking position. However, they impact the page’s click-through rate. It works more like a ‘hook’ rather than a description.
The better hook you’ve got to say, the more organic traffic your site will get. In a case where your meta description isn’t relevant, Google may choose its description for search results.
Here are some tips for writing a compelling meta description:
- Keep it short: More than 50% of people use mobile devices to browse on Google. So, you should optimize your meta descriptions for mobile devices by keeping them short (up to 120 characters).
- Include your focus keyword: Google bolds the target keyword or its synonyms found in meta descriptions. Also, it’s a good SEO practice to include your focus keyword in descriptions.
- Add a CTA: Give your coming readers a call-to-action such as “read to find out more” to invite them to your page.
- Use active voice: Using active voice not only saves your characters but also makes your message clear to the readers.
6. Add internal links
Internal links are links to pages from your site. Here’s what an internal link looks like:

Internal links are important for on-page optimization. Here’s why:
- Google gets a signal that the linked-to pages are valuable.
- People click on relevant internal links. So, if your internal link is compelling enough, site visitors may stay longer.
- Internal links allow Google crawlers to discover and navigate through new pages on your site.
- They help search engines understand your site’s structure.
7. Add external links
While internal links are linked to the pages from your site, external links point to the pages from other sites. You can add external links by adding relevant sources as we did it here:

According to Google, you should link to authoritative and relevant pages in your industry to build trust and enhance your readers’ experience. External links are a good SEO practice for this reason.
Here are some of the best practices to follow while adding external links:
- Link to only authoritative and trustworthy sites that are relevant to your niche.
- Strategically place external links to avoid looking spammy.
- Most importantly, add only the links that add value to your content.
However, in a case where you’re adding external links for the purpose of:
- Advertisement
- Or, the “you’ll link to me and I’ll link to you” arrangement
You should add the “rel=nofollow” link attribute.
8. Optimize with images
Google always encourages bloggers to include images because:
- They act as an engaging point for readers.
- They entertain and educate at the same time.
- They add value to the blog by breaking down complex concepts.
However, in blogging, uploading an image is not all you do. You also do something called “Image SEO”.
Here’s a quick summary of how you can optimize your images:
- Compress images: Don’t use high-resolution images in the PNG format. Go for the JPEG format.
- Pick good file names: Make your file name descriptive and concise, sharing what the image is about.
- Use relevant images: Add images that are relevant to the blog.
- Add alt text: Describe the image’s context. However, don’t forcefully add alt text to a decorative image. Keep it natural and try including your target keyword in the text.
Additionally, you can use image optimization and image CDN plugins.
9. Complete the word count
Going back to the first point, quality content is all that matters in SEO. So does the length of your content.
Look at your competitors’ articles, their subheadings and word count. Take inspiration, add your unique approach to it, and then start with the content.
For example, if your competitor is publishing a 2,000-word article, you should try for at least a 1500-1800 word article.
10. Make the URL slug SEO-friendly
When you’re doing the on-page SEO of a web page, you also decide the page’s slug (the URL). Usually, the slug gets formed based on your SEO title. However, you can shorten, or change it.
Follow these two tips to create an optimized slug:
- Keep the slug simple and relevant to the page for Google crawlers.
- Include the target keyword in the slug.
Bonus Points
Here are 3 bonus points to ensure that your efforts make it to the end:
- Ensure that your web pages are indexed: Indexing your site’s pages allows bots to crawl them and thus, they show in search results. You can always do so from the ‘URL inspection’ section of the Google Search Console (Read full Guide on Google Search Console)

- Your site should be responsive: More than 50% of the Google searches come from mobile devices. Therefore, your site should be accessible from every type of device (Mobile, Tablet, and Desktop).
- The page load time shouldn’t be too much: Make sure that your site’s pages load within 5 seconds otherwise you’ll see a high bounce rate.
A Quick Recap
The quickest recap ever says:
- Do keyword research properly.
- Write unique, well-researched content.
- Improve the ins and outs of your content by analyzing your competitors.
Your first step in SEO should be on-page optimization. It shouldn’t go anywhere else until later.






